How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill increasingly in demand. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of drone operation, from understanding the basic components and pre-flight checks to mastering advanced flight techniques and adhering to legal regulations. We’ll explore everything you need to know to confidently take to the skies, whether you’re a beginner or looking to refine your skills.
We’ll cover essential topics such as pre-flight procedures, understanding flight controls, navigating different flight modes, capturing stunning aerial footage, and maintaining your drone for optimal performance. Safety and legal compliance are paramount, and we’ll delve into the crucial aspects of responsible drone operation to ensure you fly legally and responsibly.
Drone Components and Their Functions
Understanding the individual components of a drone and how they work together is crucial for safe and effective operation. Each part plays a vital role in the drone’s flight capabilities and overall performance. This section details the key components, their functions, and potential issues.
Drone Component Breakdown
Let’s explore the major components of a typical drone and their interactions during flight.
| Component | Function | Importance | Potential Issues |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Generate thrust and lift, enabling flight. | Essential for flight; determines maneuverability and speed. | Damage, imbalance, insufficient thrust. |
| Motors | Power the propellers; control speed and direction. | Crucial for propulsion; directly impacts flight stability. | Motor failure, overheating, insufficient power. |
| Flight Controller | The “brain” of the drone; processes data from sensors and controls motors. | Essential for stability and control; manages all flight aspects. | Malfunction, software glitches, sensor errors. |
| Battery | Provides power to all components; flight time is directly related to battery capacity. | Essential for flight duration; impacts performance and safety. | Low battery, overheating, rapid discharge. |
| GPS | Provides location data, enabling autonomous flight and return-to-home functionality. | Important for precise positioning and safe operation, especially in open areas. | Signal loss, inaccurate positioning, interference. |
| Camera | Captures photos and videos; quality varies based on sensor and lens. | Important for the primary function of aerial photography/videography. | Image blur, low light performance issues, malfunction. |
During flight, the flight controller receives data from the GPS, sensors (like accelerometers and gyroscopes), and the remote controller. It then processes this information and sends signals to the motors, adjusting propeller speeds to maintain stability, altitude, and direction as commanded by the pilot.
Pre-Flight Checks and Procedures
A thorough pre-flight check is paramount to ensuring a safe and successful flight. Overlooking even minor details can lead to accidents. This section Artikels the essential steps and a checklist for a comprehensive pre-flight inspection.
Pre-Flight Checklist
Before each flight, meticulously check the following:
- Battery level and health
- Propeller condition (no cracks or damage)
- Motor functionality (spin each propeller individually)
- GPS signal strength and accuracy
- Camera functionality (test recording and image quality)
- Flight controller calibration and firmware updates
- Remote controller connection and battery level
- Weather conditions (wind speed, precipitation)
- Airspace restrictions and no-fly zones
Pre-Flight Procedure Flowchart
A visual representation of the pre-flight procedure helps streamline the process. The flowchart would start with “Power on drone and controller,” proceed through the checklist items (battery check, propeller inspection, etc.), and culminate in “Initiate flight” after all checks are completed successfully. A separate branch would lead to “Troubleshooting” if any issue is detected during the checklist.
Taking Off and Landing
Safe takeoff and landing procedures are fundamental to drone operation. Understanding the impact of wind and having a plan for emergencies is crucial for preventing accidents.
Takeoff and Landing Procedures
For a safe takeoff, select a clear, open area free from obstacles. Begin with a gentle throttle increase, allowing the drone to ascend slowly and steadily. Maintain visual contact at all times. Landing should be performed similarly, gradually decreasing throttle to descend smoothly and gently to the ground. Always ensure the landing area is level and free from hazards.
Wind Conditions Impact
Wind significantly affects takeoff and landing. Strong winds can make controlling the drone challenging, potentially leading to crashes. In windy conditions, it’s crucial to choose a sheltered location, adjust takeoff and landing angles to compensate for wind drift, and be prepared for potential challenges in maintaining stability.
Emergency Landing Procedures
In case of a malfunction (e.g., low battery, GPS signal loss, motor failure), initiate an emergency landing by gently lowering the drone to the ground. Prioritize safety over data recovery. If the drone becomes uncontrollable, consider activating the “return-to-home” function (if available) or prepare for a controlled crash in a safe area.
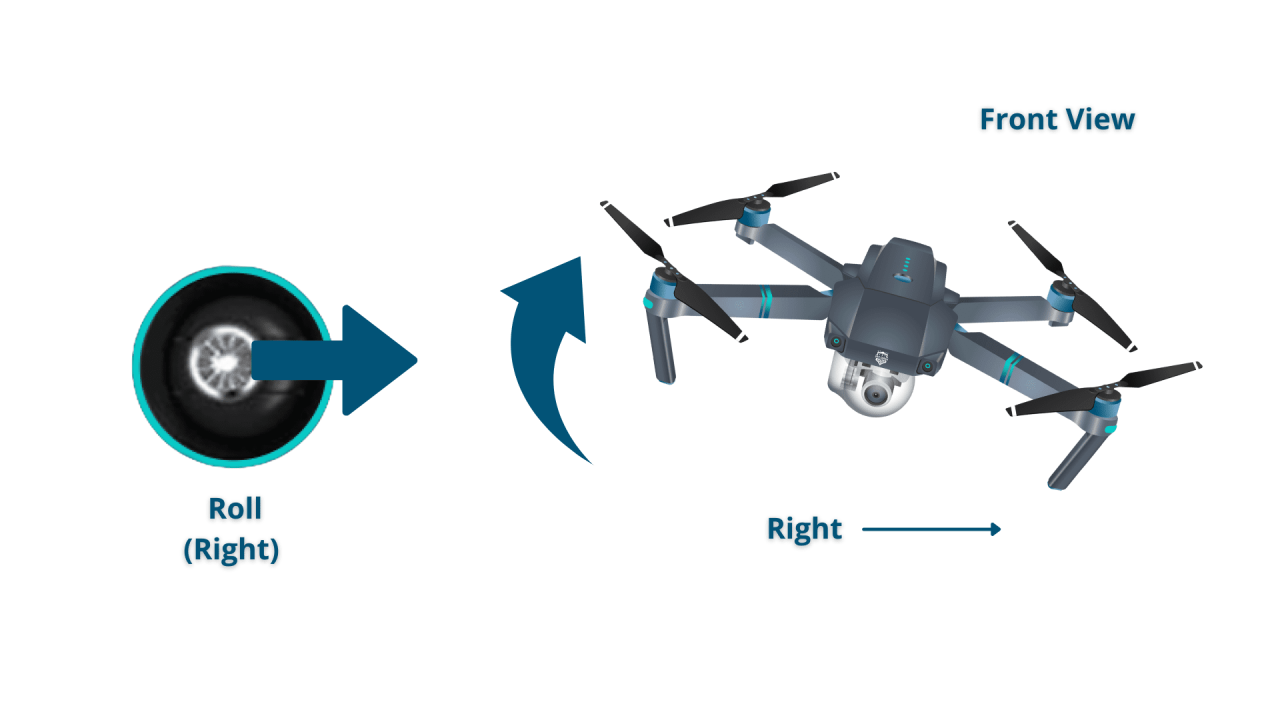
Basic Flight Controls
Understanding the basic flight controls is essential for maneuvering the drone effectively and safely. Different control interfaces exist, but the fundamental principles remain consistent.
Flight Control Stick Functions
Most drones use joysticks to control flight. Typically, one stick controls altitude (throttle) and pitch/forward/backward movement, while the other controls roll (left/right movement) and yaw (rotation). A detailed description of each stick’s function and how they interact to control the drone’s movement in three-dimensional space would be included here.
Drone Control Interfaces
While joysticks are the most common interface, some drones offer smartphone app control. A comparison of these interfaces would highlight the advantages and disadvantages of each, considering factors such as precision, ease of use, and features.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating these steps requires practice and a solid understanding of the regulations. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, including safety protocols and legal requirements, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone to improve your skills and ensure safe flights.
Ultimately, responsible drone operation hinges on thorough preparation and continuous learning.
Step-by-Step Maneuvering Guide

A step-by-step guide would detail how to use the controls to move the drone forward, backward, left, right, up, down, and rotate. It would emphasize the importance of smooth and gradual control inputs to avoid jerky movements and potential loss of control.
Advanced Flight Techniques
Mastering basic maneuvers is the foundation for more advanced techniques. Smooth and controlled movements are key to achieving professional-looking aerial footage.
Basic Maneuvers
This section would cover hovering (maintaining a steady position in the air), turning (rotating the drone smoothly), and climbing (ascending to a higher altitude) and descending. It would emphasize the importance of precise control inputs and understanding the drone’s responsiveness.
Smooth and Controlled Movements
Achieving smooth and controlled movements requires practice and a good understanding of the drone’s dynamics. Techniques like using small, incremental control inputs and anticipating the drone’s response would be discussed. The importance of avoiding sudden movements and maintaining a steady hand would also be highlighted.
Flying in Windy Conditions
Flying in windy conditions presents significant challenges. Techniques for compensating for wind drift, maintaining stability, and avoiding crashes would be discussed. Examples of strategies for adjusting flight parameters to mitigate wind effects would be provided.
Drone Camera Operation
The camera is a key feature of many drones. Understanding camera settings and modes is essential for capturing high-quality aerial photos and videos.
Camera Setting Adjustments
This section would explain how to adjust key camera settings such as resolution (e.g., 4K, 1080p), shutter speed (influencing motion blur), and ISO (controlling sensitivity to light). The impact of each setting on image quality would be discussed, along with recommendations for different shooting scenarios.
Camera Modes
Different camera modes (photo, video, timelapse) offer various creative possibilities. This section would describe each mode, explaining its purpose and how to use it effectively. Examples of when to use each mode would be provided.
Capturing High-Quality Aerial Media
Capturing high-quality aerial photos and videos requires careful planning and execution. Tips on composition, lighting, and stabilization techniques would be provided, along with examples of best practices for various shooting scenarios.
Drone Maintenance and Safety: How To Operate A Drone
Regular maintenance and safe operating practices are crucial for prolonging the lifespan of your drone and preventing accidents. This section Artikels essential maintenance procedures and safety guidelines.
Regular Maintenance Procedures

Regular maintenance includes cleaning the drone body and propellers, inspecting for damage, lubricating moving parts (if necessary), and checking battery health. A schedule for regular maintenance checks would be provided.
Safe Drone Operation and Storage
Safe operation involves always maintaining visual line of sight, avoiding flying near people or obstacles, and being aware of airspace restrictions. Proper storage involves keeping the drone in a dry, safe place, away from extreme temperatures and potential damage.
Potential Drone Malfunctions and Troubleshooting
- Low Battery: Charge the battery fully. Consider shortening flight times.
- GPS Signal Loss: Fly in an open area with a clear view of the sky. Check for GPS interference.
- Motor Failure: Inspect motors for damage. Replace faulty motors.
- Propeller Damage: Replace damaged propellers. Ensure proper balance.
- Flight Controller Issues: Recalibrate the flight controller. Update firmware if necessary.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Operating a drone responsibly requires understanding and adhering to local laws and regulations. This section highlights the importance of legal compliance and provides resources for obtaining necessary permits and licenses.
Importance of Understanding Local Regulations
Drone regulations vary by location. Failing to comply with these regulations can result in fines, legal action, or even criminal charges. It’s crucial to research and understand the specific rules and regulations in your area before flying.
Airspace Restrictions and No-Fly Zones
Many areas have airspace restrictions or no-fly zones, such as airports, military bases, and sensitive areas. These restrictions are in place to ensure safety and security. It is essential to check for these restrictions before each flight using online resources or mobile applications.
Resources for Obtaining Permits and Licenses
Depending on the type of drone operation and location, you may need to obtain permits or licenses. Resources for finding and obtaining these permits would be listed here, including relevant government websites and aviation authorities.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Issues
Even with careful maintenance and operation, drones can experience problems. This section Artikels common issues, their causes, solutions, and preventative measures.
Common Drone Problems and Solutions, How to operate a drone
| Problem | Cause | Solution | Prevention |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low Battery | Insufficient charge, high power consumption | Charge battery fully; reduce flight time | Regular battery maintenance, monitor battery health |
| GPS Signal Loss | Obstructions, interference, weak signal | Fly in open area, restart drone, check for interference | Avoid flying in cluttered environments |
| Motor Failure | Physical damage, overheating | Inspect and replace faulty motors | Regular inspection, avoid overheating |
| Propeller Damage | Collisions, wear and tear | Replace damaged propellers | Careful flight operation, regular inspection |
| Flight Controller Malfunction | Software glitches, hardware failure | Recalibrate, update firmware, contact manufacturer | Regular firmware updates, careful handling |
Illustrating Drone Flight Paths
Planning a drone flight path is crucial for capturing desired footage and ensuring safe operation. This section describes the process and provides a sample flight path illustration.
Drone Flight Path Planning
Planning involves considering factors such as the desired shots, the location, weather conditions, and any airspace restrictions. Using mapping software or apps can help visualize the flight path and ensure it is safe and legal. The process includes defining waypoints (locations the drone will fly to), altitudes, and speeds.
Sample Flight Path
A sample flight path might start at a designated takeoff point (e.g., a field), ascend to a specified altitude (e.g., 50 meters), then fly horizontally along a straight line for a distance (e.g., 100 meters). After reaching the end of the straight line, the drone would execute a gentle 90-degree turn to the right, continue along another straight line (e.g., 50 meters), and then slowly descend to the ground for landing at a designated landing point.
Altitude changes and turning points would be clearly defined in a detailed description, providing sufficient information to create a visual representation.
Mastering drone operation requires a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical experience. By understanding the mechanics of your drone, practicing safe flight procedures, and adhering to regulations, you can unlock the exciting possibilities of aerial photography and videography. Remember that continuous learning and responsible piloting are key to a successful and enjoyable drone experience. Safe and happy flying!
FAQ Corner
What is the best drone for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones are available for beginners. Look for models with features like GPS stabilization, automatic return-to-home, and intuitive control apps.
How long does a drone battery last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the model and flight conditions. Expect flight times ranging from 15 to 30 minutes, often less in windy conditions or with heavy camera use.
What happens if I lose GPS signal?
Most modern drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function. If GPS is lost, the drone will attempt to return to its takeoff point. However, always maintain visual contact and be prepared to take manual control if needed.
How do I register my drone?
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers. Mastering the art of drone operation requires practice and patience, but the rewards of capturing stunning aerial footage are well worth the effort.
Registration requirements vary by country and region. Check with your local aviation authority for specific regulations and procedures. Many countries require registration for drones above a certain weight.
